
When you boil it down, the purpose of ISO 27001 is pretty straightforward. Identify the security incidents that could affect your business. Then find the best ways to either keep those incidents from happening or lessen their impact.
Risk assessments are essential to that purpose. Without one, you won’t have the knowledge you need to build a secure information security management system in the first place, let alone get ISO 27001 certified.
In this post, we’ll lay out the step-by-step process of completing an ISO 27001 risk assessment.
And we’ll share some tips, templates, and resources to help simplify and streamline things along the way.
A risk assessment is a requirement for the ISO 27001 standard. If you want to be ISO 27001 certified, you’ll need to:
A risk treatment plan involves deciding how you will respond to each risk to keep your business secure.
Together, your risk assessment and your risk treatment plan make up your overall ISO 27001 risk management process.
ISO 27001 risk assessment requirements include:

ISO 27001 Certification Costs
To meet ISO 27001 certification requirements, your ISO 27001 risk assessment procedure should follow these steps:
How will you identify and respond to information security risk? How will you estimate likelihood and impact? What is your company’s acceptable level of risk?
In general, there are two approaches to risk assessment: qualitative and quantitative.
With a qualitative approach, you’ll go through different scenarios and answer “what if” questions to identify risks. A quantitative approach uses data and numbers to define levels of risk.
Some common risk management frameworks include ISO 27005:2018, OCTAVE, and NIST SP 800-30 Revision 1.
Whichever approach or methodology you choose, company management should be closely involved in this process. They’ll be instrumental in determining your organization’s baseline security criteria and level of acceptable risk.
And by establishing your risk management methodology at the company level, every department will be able to follow the same cohesive process.
Start with a list of information assets and then identify risks that could impact data confidentiality, integrity, and availability for each one. You’ll need to consider your hardware (including mobile devices), software, information databases, and intellectual property.
Once you’ve identified a set of risks, determine the potential likelihood of each one occurring and its business impact. Remember that impact isn’t always monetary — it could be an impact on your brand’s reputation and customer relationships, a legal or contractual issue, or a threat to your compliance.
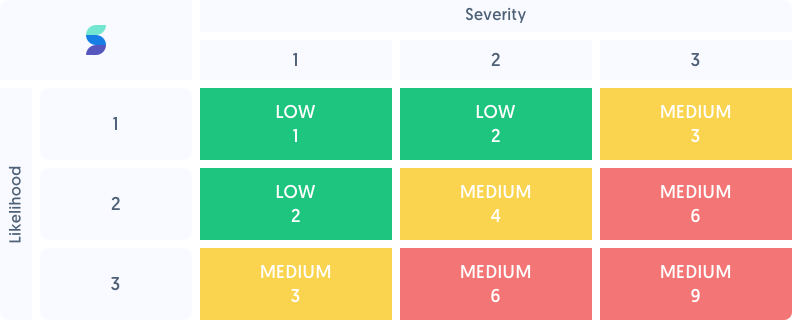
Assign each risk a likelihood and impact score. On a scale from 1-10, how probable is it that the incident will occur? How significant would its impact be? These scores will help you prioritize risks in the next step.
No business has unlimited resources. You’ll need to decide which risks you should spend time, money, and effort to address and which fall within your acceptable level of risk.
Now that you’ve analyzed the likelihood and impact of each risk, you can use those scores to prioritize your risk management efforts. A risk matrix can be a helpful tool in visualizing these priorities.
The risk treatment plan is an essential document for ISO 27001 certification, and it’s one your certification auditor will want to review. It records how your organization has decided to respond to the threats you identified in your risk assessment.
The ISO 27001 standard outlines four possible actions:
ISO 27001 also requires that each risk have an established owner. The owner will be responsible for approving your treatment plan for that risk and accepting any residual risk.
Your certification auditor will likely want to review evidence that you’ve completed your risk management process. These documents may include a risk assessment report and a risk summary report.
The ISO 27001 risk assessment report provides an overview of your risk assessment process, including which information assets you evaluated, which risk treatment option you selected for each identified risk, and the probability and impact scores for each.
The risk summary details the risks that your organization is choosing to address after completing the risk treatment process.
Continuous improvement is one of the central ideas of the ISO 27001 standard. You’ll need to make conducting these risk assessments an ongoing process.
Monitoring and assessing risk should be incorporated into the day-to-day habits of your team. That said, the recommended formal ISO 27001 risk assessment frequency is once a year, ideally when you conduct your internal audit.
Internal auditors should consider any new risks that have emerged and evaluate how well your current risk management program is working to safeguard your ISMS.
This editable spreadsheet will guide you through the process of creating an asset register, assigning asset and risk owners, identifying and scoring risks, and selecting your risk treatment. It includes a built-in risk matrix to help you quickly visualize high-priority risks and build out your remediation plan.

Want to skip the spreadsheets?
Our compliance automation platform guides you through the risk assessment process and automatically generates an ISO 27001 readiness report. You’ll be able to see exactly how close you are to achieving certification and get actionable advice for closing any gaps.
Request a demo with one of our product experts today.